EXPLORE EVIDENCE
Envisia evidence library
Publications and Abstracts
Envisia has been clinically and analytically validated, and has shown utility through clinical utility studies and real world evidence.

- December 2023
- PUBLICATION
- Fayez Kheir, MD, et al.
CHEST Pulmonary
Retrospective analysis of patients in a multi-center study assessing change in management strategy following Envisia and cryobiopsy and the association between Envisia UIP classification and disease progression. Results showed combining Envisia with Cryobiopsy demonstrated meaningful impact on therapeutic strategy for ILD patients. Envisia positive patients who were not prescribed antifibrotics were twice as likely to progress compared to Envisia negative patients.

- October 2023
- POSTER DISCUSSION
- J. Chung, et al.
CHEST 2023 Conference
HRCTs were independently read by two expert thoracic radiologists in the BRAVE study in 74 patient ILD cases. Inter-reader variability was notable when interpreting HRCT findings. This data highlights the need for multi-disciplinary approaches and additional testing modalities, such as a genomic classifier or histopathology, to establish a confident clinical diagnosis in these patients rather than relying on HRCT alone.

- May 2023
- POSTER DISCUSSION
- Lisa Lancaster, MD et al.
ATS 2023 Conference
Findings from a retrospective analysis of 135 patients from the BRAVE trial examined the impact of an Envisia Genomic Classifier result on FVC progression at 12 months. The study found that Envisia may serve as a biomarker of progression across a range of ILD patients and could prompt earlier treatment intervention to slow progression.

- May 2023
- POSTER
- Diana Espinoza Barrera, MD, et al.
ATS 2023 Conference
In an independent, multi-center study, researchers retrospectively analyzed data for 98 patients with ILD that underwent a clinically indicated bronchoscopy with cryobiopsy and the Envisia Genomic Classifier to assess change in management. The authors concluded that adding Envisia to cryobiopsy demonstrated a meaningful impact on therapeutic intervention with a 76% change in management strategy with more patients being started on antifibrotic therapy following a positive Envisia result.
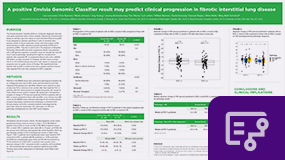
- October 2022
- POSTER
- Lisa Lancaster, MD et al.
CHEST 2022 Conference
The Envisia classifier positive result may serve as a biomarker for FVC by identifying the genomic signature of UIP in patients without definite UIP on CT. Results for the study showed that patients with an Envisia positive result show a greater decline in FVC over time compared to Envisia negative patients. The Envisia classifier could have utility in identifying patients with IPF and non-IPF progressive pulmonary fibrosis and underlying UIP earlier in their disease, allowing for aggressive therapy before significant, irreversible FVC loss.
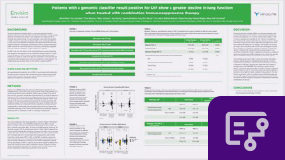
- September 2022
- POSTER
- Athol Wells, MD et al.
European Respiratory Society
Researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 135 patients enrolled in the BRAVE trial who underwent evaluation for an undiagnosed ILD, had an Envisia Genomic Classifier result, and had multiple forced vital capacity (FVC) measurements to assess lung function over time. These findings show that an Envisia positive result may help identify patients in whom two drug immunosuppressive therapy is harmful. These results further support the utility of Envisia, highlighting the potential of an Envisia positive result to inform both diagnosis and treatment decisions, identifying patients in whom antifibrotic therapy may be preferred.

- May 2022
- PUBLICATION
- Fayez Kheir, MD, et al.
Annals of the American Thoracic Society
This systematic review summarizes four published studies in which the Envisia classifier identified UIP with a combined 92% specificity and 68% sensitivity compared to histopathologic UIP to confidently inform UIP and provide important diagnostic information. Confidence in diagnosing IPF was significantly improved in two separate studies when the Envisia classifier result was added to clinical factors and HRCT.
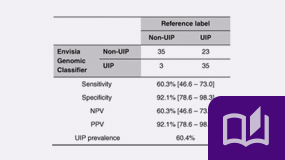
- July 2020
- PUBLICATION
- Luca Richeldi, et al.
American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
In 96 patients with suspected ILD the Envisia Genomic Classifier identified UIP regardless of HRCT pattern. These results suggest that recognition of a UIP pattern by Envisia combined with HRCT and clinical factors in a multidisciplinary discussion may assist clinicians in making an interstitial lung disease (especially IPF) diagnosis without the need for a surgical lung biopsy.

- April 2019
- PUBLICATION
- Ganesh Raghu, et al.
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Envisia identified usual interstitial pneumonia in transbronchial lung biopsy samples from 49 patients with 88% specificity and 70% sensitivity.

- June 2022
- PUBLICATION
- Joseph A. Lasky, et al.
Annals of the American Thoracic Society
The clinical utility data confirms the use of the Envisia Classifier to increase physician confidence in diagnosis of IPF, and recommendation for antifibrotic therapy, while also reducing invasive and potentially risky surgical lung biopsies (SLBs).

- May 2021
- PUBLICATION
- Luca Richeldi, et al.
American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
The Envisia Genomic Classifier Demonstrates Consistent Performance Across Gender, Age Group, and Smoking Status
Hear from peers
Discover what key opinion leaders are saying about Envisia in case studies, testimonials or on-demand presentations.

